The Most Impressive Achievement of the Harappan Culture, Ranked
Voting rules: Choose the achievement you think is the most impressive!

Updated on Apr 28, 2024 06:27
In a quiet corner of history, nestled between the well-trodden paths of ancient civilizations, the Harappan culture carved out a niche of remarkable ingenuity. Understanding which of their achievements most captivates us today can provide insights into what we value as innovative or pivotal. Ranking these achievements helps to highlight the attributes we consider most valuable in cultural and historical advancements.
By casting a vote for what you believe stands out as the most impressive feat of the Harappan culture, you contribute to a collective assessment of its historical significance. This process not only deepens our appreciation for the culture but also influences how it is perceived and taught in our modern context. The resulting list can serve as a reflection of contemporary values and interests surroundng ancient civilizations.
What Is the Most Impressive Achievement of the Harappan Culture?
-
170votesThe Harappan civilization was known for its impressive urban planning, with well-planned streets, drainage systems, and public buildings.The Indus Valley Civilization's Urban Planning was an incredible achievement of the Harappan culture. It involved the construction and layout of their cities and towns, showcasing advanced knowledge and skills in city planning. The urban planning of the Indus Valley Civilization was truly remarkable and demonstrated their ability to create and maintain well-organized and efficient urban centers.
- Planned Cities: The cities of the Indus Valley Civilization were meticulously planned, with well-organized street grids and layout.
- Advanced Drainage System: The cities had an advanced and sophisticated drainage system, consisting of covered drains and sewers that were connected to the houses.
- Well-structured Buildings: The houses and buildings in these cities were made of high-quality brick and featured multiple stories. They were designed with specific areas for different purposes, such as living quarters, kitchens, and bathrooms.
- Public Wells: There were numerous public wells strategically placed throughout the cities, providing access to clean water for all residents.
- Citadel and Lower Towns: The cities were often divided into two sections - the citadel, which was erected on an elevated platform and served as the administrative and religious center, and the lower town, where residential and commercial activities were concentrated.
-
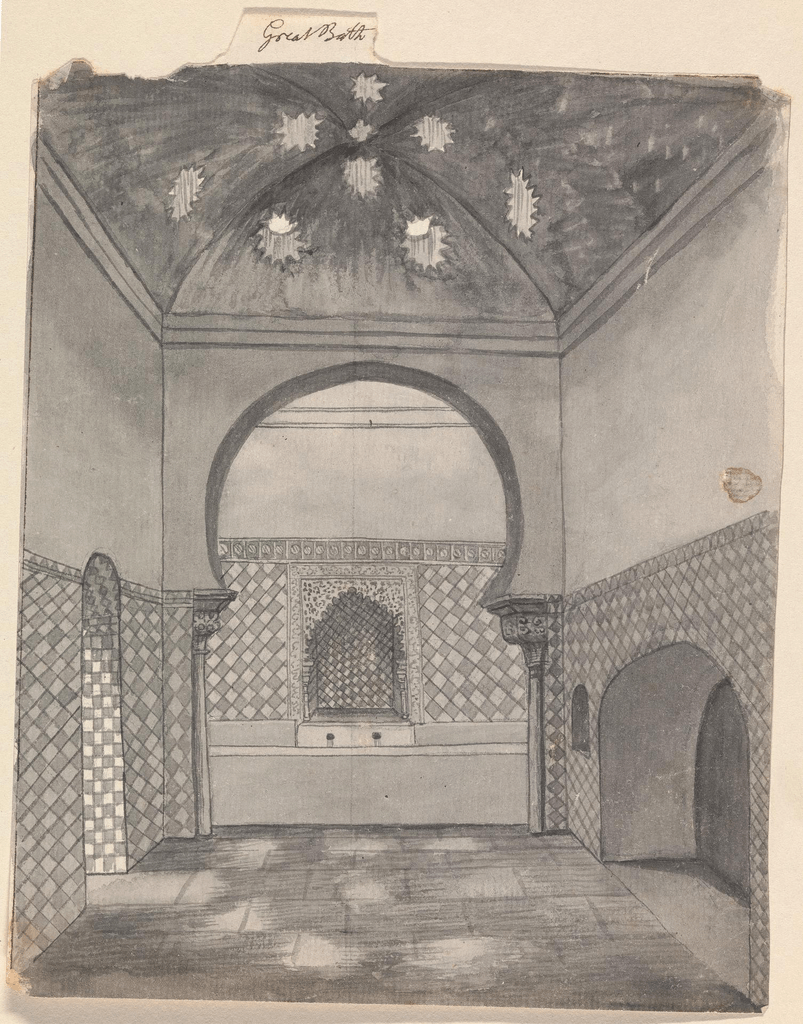
240votesThe Great Bath in Mohenjo-Daro is a remarkable feat of engineering, with waterproofed walls and a sophisticated drainage system.The Great Bath was a large and impressive structure located in the ancient city of Mohenjo-daro, which was part of the Harappan culture in the Indus Valley Civilization. It was built around 2500 BCE and is considered one of the most remarkable achievements of the Harappan people.
- Size: The Great Bath measures approximately 12 meters long, 7 meters wide, and 2.4 meters deep.
- Materials: It was constructed using tightly fitted bricks of uniform size, with a layer of natural tar serving as a waterproofing agent.
- Layout: The bath consisted of two main sections: a large pool area, which was lined with bricks and provided space for people to enter and bathe, and a smaller raised platform believed to be used for religious or ceremonial purposes.
- Drainage System: The Great Bath had a complex and efficient drainage system, with interconnected channels and drains that allowed water to be emptied and replenished regularly.
- Steps: The pool area of the bath had steps on all four sides, providing easy access for people to enter the water.
-
315votesThe Harappan civilization had a script that is yet to be fully deciphered, but it is considered one of the earliest known writing systems in the world.The Writing System of the Harappan culture is one of their most impressive achievements. It is an ancient script that remains undeciphered to this day, making it a mystery that scholars continue to study and explore. The writing system consists of a series of symbols or characters that were typically engraved or inscribed on various mediums such as pottery, seals, and copper tablets.
- Undeciphered Script: The writing system of the Harappan culture remains undeciphered, adding to its intrigue and importance in understanding this ancient civilization.
- Logographic Script: The Harappan script is believed to be a logographic script, where each symbol denotes a word or concept rather than individual sounds.
- Linear Directionality: The script typically follows a linear direction from right to left or left to right, resembling the appearance of modern writing systems.
- Hundreds of Characters: The Harappan script consists of several hundred unique characters or symbols, making it a complex writing system.
- Lack of Bilingual Inscriptions: One of the challenges in deciphering the script is the absence of bilingual inscriptions, which hampers the comparison with known languages.
-
419votes
Trade Networks
Harappan merchants and tradersThe Harappan civilization had a vast trade network that spanned across the Indian subcontinent and beyond, with evidence of trade with Mesopotamia and Egypt.The trade networks of the Harappan culture refers to the extensive and sophisticated trading routes that connected the Harappan civilization to various regions in ancient Mesopotamia, Central Asia, and the Arabian Peninsula.- Geographical Reach: Covered regions across present-day Pakistan, India, Iran, Afghanistan, Mesopotamia, Central Asia, and the Arabian Peninsula.
- Long-Distance Trade: Enabled long-distance trade, including the exchange of goods such as textiles, pottery, precious stones, metals, and agricultural products.
- Maritime Routes: Utilized maritime routes through the Persian Gulf, facilitating trade with the ancient civilizations of Sumer, Akkad, Elam, and Dilmun.
- Urban Centers as Hubs: Major Harappan urban centers, such as Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, served as crucial trade hubs where goods were exchanged and redistributed.
- Trade Tokens: Use of standardized trade tokens, such as small clay seals, possibly indicating a system of weights and measures for trade.
-
514votesThe Harappans were skilled farmers who used advanced techniques such as crop rotation and irrigation to increase agricultural productivity.The agricultural practices of the Harappan culture were highly advanced for their time, contributing to the prosperity and sustainability of their civilization. The Harappans made significant advancements in farming techniques, crop cultivation, and irrigation systems.
- Crop diversity: The Harappans cultivated a wide variety of crops including wheat, barley, peas, sesame, mustard, and cotton.
- Planned agriculture: They had well-planned layouts for fields and well-defined irrigation systems, ensuring efficient water distribution and crop management.
- Advanced irrigation: The construction of dams, reservoirs, and canals allowed for controlled irrigation, benefiting both crops and livestock.
- Sustainable practices: The Harappans practiced crop rotation, allowing the soil to rejuvenate and maintain its fertility over time.
- Use of plows: They used wooden plows pulled by oxen to till the land, increasing efficiency and productivity in farming.
-
68votesThe Harappan civilization produced exquisite art and crafts, including pottery, jewelry, and figurines.
-
714votesThe Harappan civilization had a complex social organization with a hierarchical system of governance and a sophisticated legal system.The social organization of the Harappan culture was a complex system that provided structure and order to their society. It encompassed various aspects such as social classes, governance, and occupations.
- Urban planning: Cities like Mohenjo-daro and Harappa were well-planned and had sophisticated grid systems.
- Citadel: Each city had a fortified citadel, likely serving as a central administrative and religious hub.
- Social hierarchy: There was evidence of a hierarchical social structure, with elite classes and commoners.
- Craft specialization: The society had specialized craftsmen, including potters, weavers, metalworkers, and beadmakers.
- Trade networks: The Harappans had extensive trade networks, evidenced by the presence of exotic goods from distant regions.
-
83votesThe Harappan civilization had a highly developed system of sanitation, with toilets and waste disposal systems in every house.Sanitation was a remarkable achievement of the Harappan culture, demonstrating their advanced urban planning and engineering skills. It involved the sophisticated management of waste disposal and the provision of a well-organized drainage system. The Harappans recognized the importance of cleanliness and took significant measures to maintain hygienic living conditions.
- 1: Well-designed sewage and drainage system
- 2: Sophisticated underground sewerage networks
- 3: Advanced public and private toilets
- 4: Flush toilets with integrated water flow
- 5: Waste management and disposal systems
-
97votesThe Harappan civilization was known for its metalworking skills, including the production of copper and bronze artifacts.Metalworking is a highly challenging art medium that involves working with various types of metals to create sculptures, structures, and decorative or functional objects. It is known for its intricate processes, requiring expertise in shaping, cutting, joining, and finishing metal materials.
- Material: Utilizes metals such as steel, iron, copper, bronze, aluminum, and precious metals.
- Techniques: Includes forging, welding, casting, soldering, riveting, engraving, etching, and hammering.
- Tools: Requires a wide range of tools, including hammers, anvils, tongs, chisels, welders, grinders, and various shaping and cutting tools.
- Heat Control: Involves precise control of temperature to heat and shape metal, often using techniques like annealing, quenching, and tempering.
- Safety Measures: Due to handling hot metals and working with sharp tools, metalworking requires adherence to safety protocols, including protective gear like gloves, goggles, and respirators.
-
106votesThe Harappan civilization had a complex religious belief system, with evidence of worship of deities such as Mother Goddess and the Horned God.The religious beliefs of the Harappan culture were an integral part of their society, shaping their worldview and impacting various aspects of their daily lives. These beliefs were centered around a complex system of deities and rituals.
- Polytheistic Beliefs: Worshiped multiple deities
- Mother Goddess: Emphasized the worship of a Mother Goddess figure
- Animal Worship: Respected and worshiped animals, possibly considering them as divine
- Ritual Baths: Engaged in ritual purification through bathing
- Fire Worship: Considered fire as a sacred element and likely practiced fire rituals
Missing your favorite achievement?
Graphs
Discussion
Ranking factors for impressive achievement
-
Urban planning and architectureThe Harappan culture, also known as the Indus Valley Civilization, exhibited an advanced understanding of urban planning and architecture. Their cities, such as Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, were carefully planned and organized, featuring grid-like street systems, standardized building materials and designs, as well as advanced systems of drainage and sanitation.
-
Social organization and administrationThe Indus Valley Civilization seemed to have employed a well-organized administrative system for managing its society, as evidenced by the cohesiveness of city planning and the standardization of weights and measures for economic exchanges.
-
Economic activities and tradeHarappan civilization had a thriving economy, characterized by agricultural productivity as well as specialization in crafts and industries like metallurgy, pottery, and bead-making. They engaged in trade with neighboring civilizations, such as Mesopotamia, and developed an extensive maritime trading network.
-
Writing and communicationThe Indus Valley Civilization developed a script, made up of more than 400 symbols, which is still undeciphered. The presence of this script on seals, pottery, and other artifacts indicates that the Harappan people possessed a form of written communication for administrative, economic, or religious purposes.
-
Art and craftsmanshipThe Harappan culture produced intricate and sophisticated works of art in the form of figurines, pottery, and seals. These artifacts reflect their skills in craftsmanship, as well as reveal aspects of their religion and belief systems.
-
Technological advancementsThe Harappan civilization showcased technological advancements in various fields, from the development of metallurgy techniques to the creation of an efficient drainage and sanitation system in their cities. These innovations contributed to the overall development of their society.
-
Religious practices and beliefsThe Harappan culture had a rich religious life, as evidenced by various artifacts and structures, including terracotta figurines and seal carvings. Some of these religious beliefs may have influenced later Indian religions, such as Hinduism.
-
Endurance and resilienceThe Indus Valley Civilization existed for approximately two thousand years (from around 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE) and maintained a remarkable level of continuity and organization throughout its existence. This demonstrates the resilience of their social structures and the strength of their cultural identity.
-
Influence on later culturesElements of the Harappan culture, such as religious beliefs and architectural styles, can be seen in later South Asian civilizations, illustrating the lasting impact of their achievements on the region's cultural and historical development.
-
Mystery and intrigueFinally, the fact that many aspects of the Harappan culture remain unknown, including the reasons for its decline and the meaning of its script, adds an element of intrigue and interest to the study of this ancient civilization.
About this ranking
This is a community-based ranking of the most impressive achievement of the Harappan culture. We do our best to provide fair voting, but it is not intended to be exhaustive. So if you notice something or achievement is missing, feel free to help improve the ranking!
Statistics
- 2351 views
- 194 votes
- 10 ranked items
Movers & Shakers
Voting Rules
A participant may cast an up or down vote for each achievement once every 24 hours. The rank of each achievement is then calculated from the weighted sum of all up and down votes.
More information on most impressive achievement of the harappan culture
The Harappan culture, also known as the Indus Valley Civilization, was one of the most advanced and impressive civilizations of the Bronze Age. Flourishing from around 2600 to 1900 BCE, this ancient civilization was spread across modern-day Pakistan and India, covering an area of more than 1.25 million square kilometers. The Harappan culture was characterized by its advanced urban planning, sophisticated architecture, and intricate systems of trade and commerce. They were also known for their impressive achievements in the fields of metallurgy, pottery, and textile production. However, perhaps the most impressive achievement of the Harappan culture was their development of a complex and sophisticated system of writing, known as the Indus script, which remains one of the most enigmatic and mysterious scripts in the world. Despite the many challenges in deciphering this ancient writing system, the Indus script remains a testament to the remarkable intellectual and cultural achievements of the Harappan people.
Explore other rankings
Check out some of the other recommended rankings on StrawPoll and make your voice heard.